前言
开心一刻
一名劫匪慌忙中窜上了一辆车的后座,上车后发现主驾和副驾的一男一女疑惑地回头看着他,他立即拔出枪威胁到:“赶快开车,甩掉后面的警车,否则老子一枪崩了你!”,于是副驾上的男人转过脸对那女的说:“大姐,别慌,听我口令把刚才的动作再练习一遍,挂一档,轻松离合,轻踩油门,走...走,哎 走...哎,哎,对,走走... 最后,三人都躺到了医院,劫匪的手上还戴上了铐子...
前情回顾
估摸着大家已经忘记了createApplicationContext的内容,本文不做过多的回顾,只是提醒大家:在AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的实例化过程中,实例化了AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader,另外也将ConfigurationClassPostProcessor定义注册到了beanFactory中,如下图所示
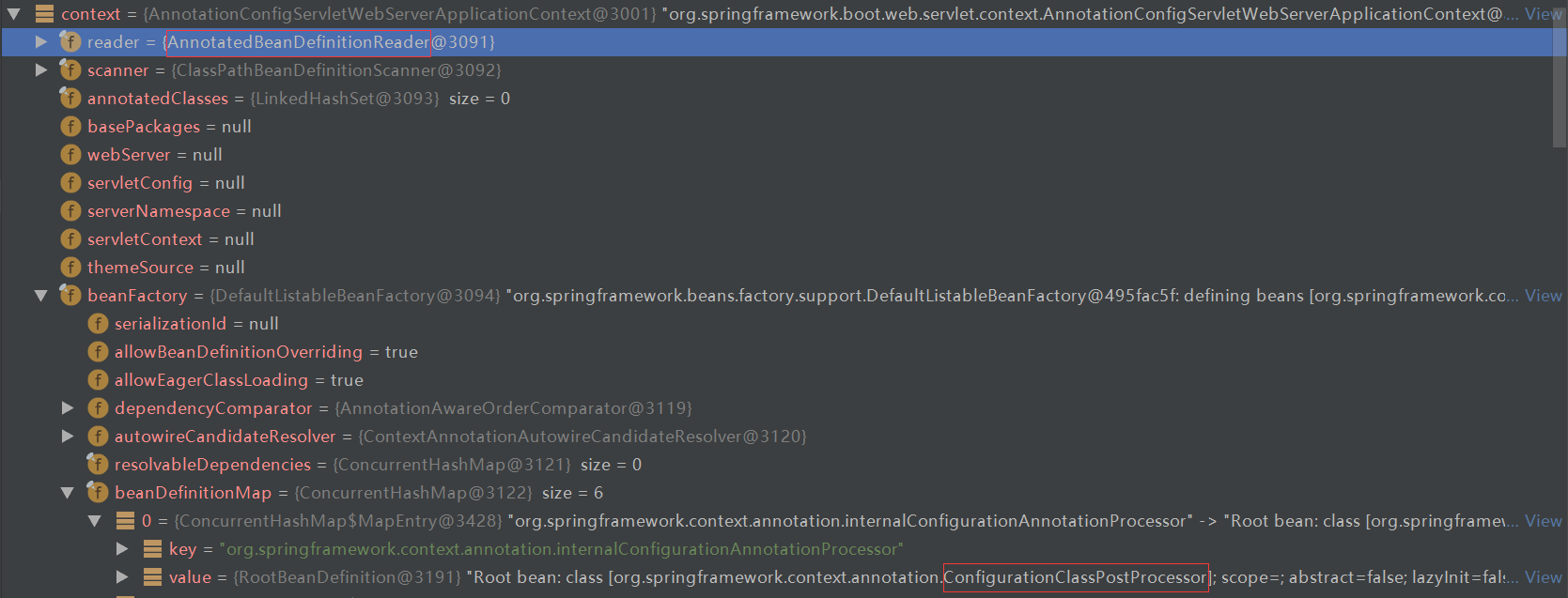
看着AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor是不是隐约感觉到了什么?
概念介绍与应用
@Configuration
- @Target(ElementType.TYPE)
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- @Documented
- @Component
- public @interface Configuration {
- /**
- * Explicitly specify the name of the Spring bean definition associated
- * with this Configuration class. If left unspecified (the common case),
- * a bean name will be automatically generated.
- * <p>The custom name applies only if the Configuration class is picked up via
- * component scanning or supplied directly to a {@link AnnotationConfigApplicationContext}.
- * If the Configuration class is registered as a traditional XML bean definition,
- * the name/id of the bean element will take precedence.
- * @return the suggested component name, if any (or empty String otherwise)
- * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultBeanNameGenerator
- */
- @AliasFor(annotation = Component.class)
- String value() default "";
- }
View Code @Configuration能够修饰Class、interface和enum,用的最多的还是标注在类上,相当于把该类作为spring的xml配置文件中的<beans>,用于配置spring容器;@Configuration往往会结合@Bean来使用,@Bean等价于spring的xml配置文件中的<bean>,用于注册bean对象。@Configuration和@Bean组成了基于java类的配置,是spring的推荐配置方式。最简单的使用如下
- @Configuration
- public class MyConfiguration {
- @Bean
- public Cat mycat() {
- return new Cat();
- }
- }
如上代码就会在spring容器中注册一个名叫mycat的Cat类型的Bean
Condition


- @FunctionalInterface
- public interface Condition {
- /**
- * Determine if the condition matches.
- * @param context the condition context
- * @param metadata metadata of the {@link org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata class}
- * or {@link org.springframework.core.type.MethodMetadata method} being checked
- * @return {@code true} if the condition matches and the component can be registered,
- * or {@code false} to veto the annotated component's registration
- */
- boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);
- }
View Code Spring的条件化配置,当我们向spring注册bean时,可以对这个bean添加一定的自定义条件,当满足这个条件时注册这个bean,否则不注册。springboot中部分实现子类如下
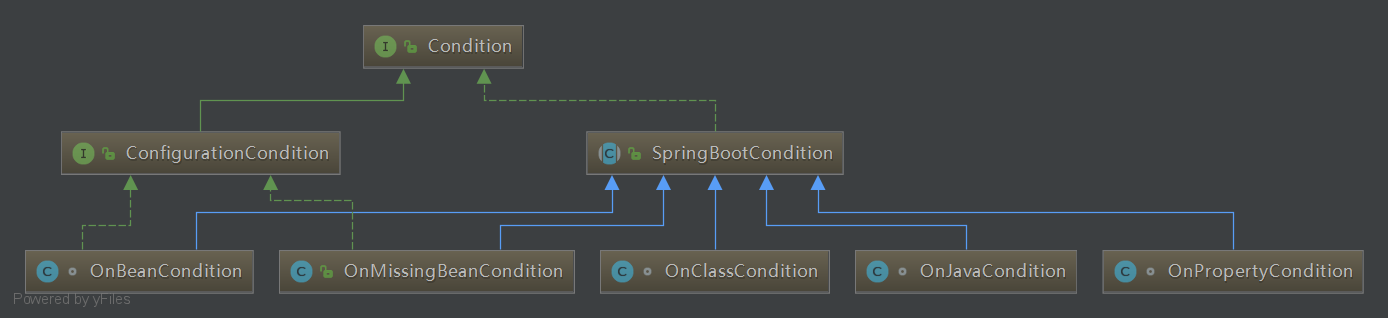
springboot更多实现请查看org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition包。Condition一般配合@Conditional使用,更多信息往下看
@Conditional


- @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- @Documented
- public @interface Conditional {
- /**
- * All {@link Condition}s that must {@linkplain Condition#matches match}
- * in order for the component to be registered.
- */
- Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
- }
View Code Spring的条件注解,其value是一个Class<? extends Condition>[],只有数组中的全部Condition全部匹配成功时,被@Conditional修饰的组件才会被注册到Spring容器中。@Conditional只是一个标志,标示需要进行条件判断,而具体的判断规则则由具体的Condition来实现。
在SpringBoot源码中很容易看到被@Conditional注解的组合注解,例如:@ConditionalOnBean、@ConditionalOnMissingBean、@ConditionalOnClass、@ConditionalOnMissingClass等,具体如下
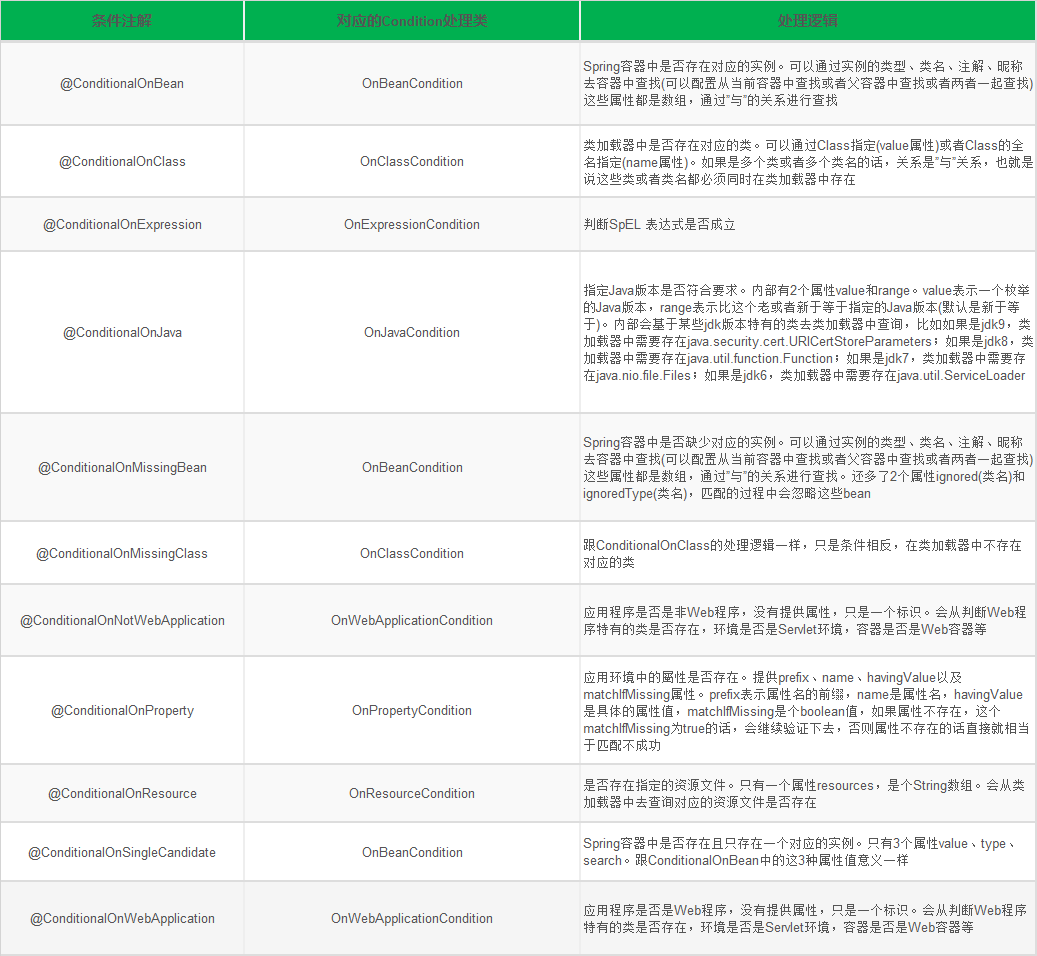
springboot还提供了AutoConfigureAfter、AutoConfigureBefore、AutoConfigureOrder,看名字基本知道其作用,具体细节需要大家自己去跟了。
完整应用案例
接口都能访问通,数据返回也都正确,非常完美
完整工程代码:spring-boot-condition
当我们把MyConfiguration中的myCat方法注释掉(ConditionWeb中的cat相关也注释掉),再启动应用的时候,应用报错启动不起来,提示如下信息:


- Description:
- Field dog in com.lee.condition.web.ConditionWeb required a bean of type 'com.lee.condition.model.Dog' that could not be found.
- - Bean method 'myDog' in 'MyConfiguration' not loaded because @ConditionalOnBean (types: com.lee.condition.model.Cat; SearchStrategy: all) did not find any beans of type com.lee.condition.model.Cat
- Action:
- Consider revisiting the conditions above or defining a bean of type 'com.lee.condition.model.Dog' in your configuration.
View Code ConditionWeb中需要Dog类型的bean,而Dog实例化又依赖Cat实例,而我们没有实例化Cat,所以应用启动报错,提示如上信息
源码探究
我们要探究什么了?不探究太细,就探究@Configuration修饰的配置类是何时解析的,@Conditional是何时生效、如何生效的
@Configuration修饰的配置类是何时解析的
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor(可以查看ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的类继承结构图),那么我们从AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法调用的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法开始
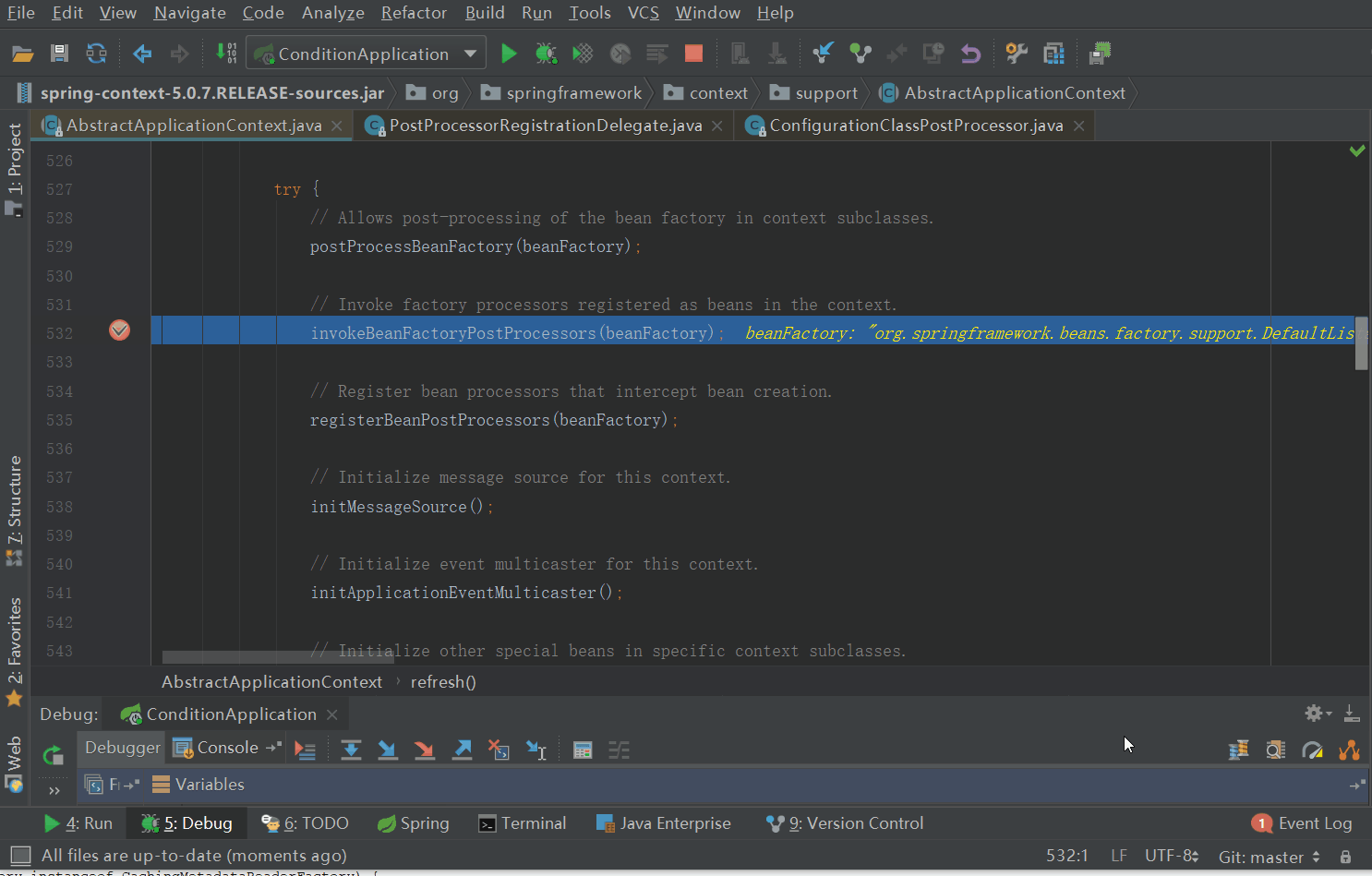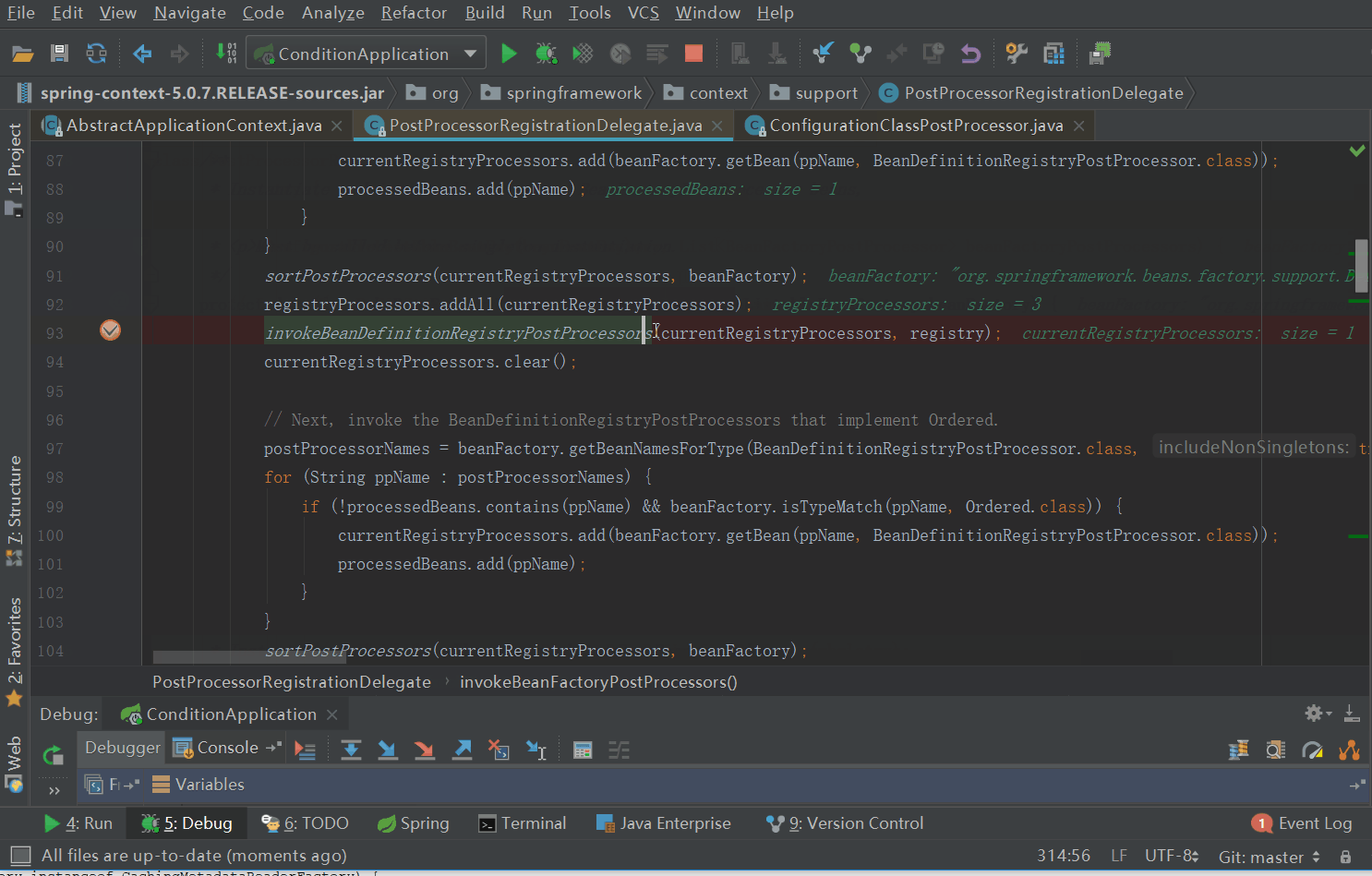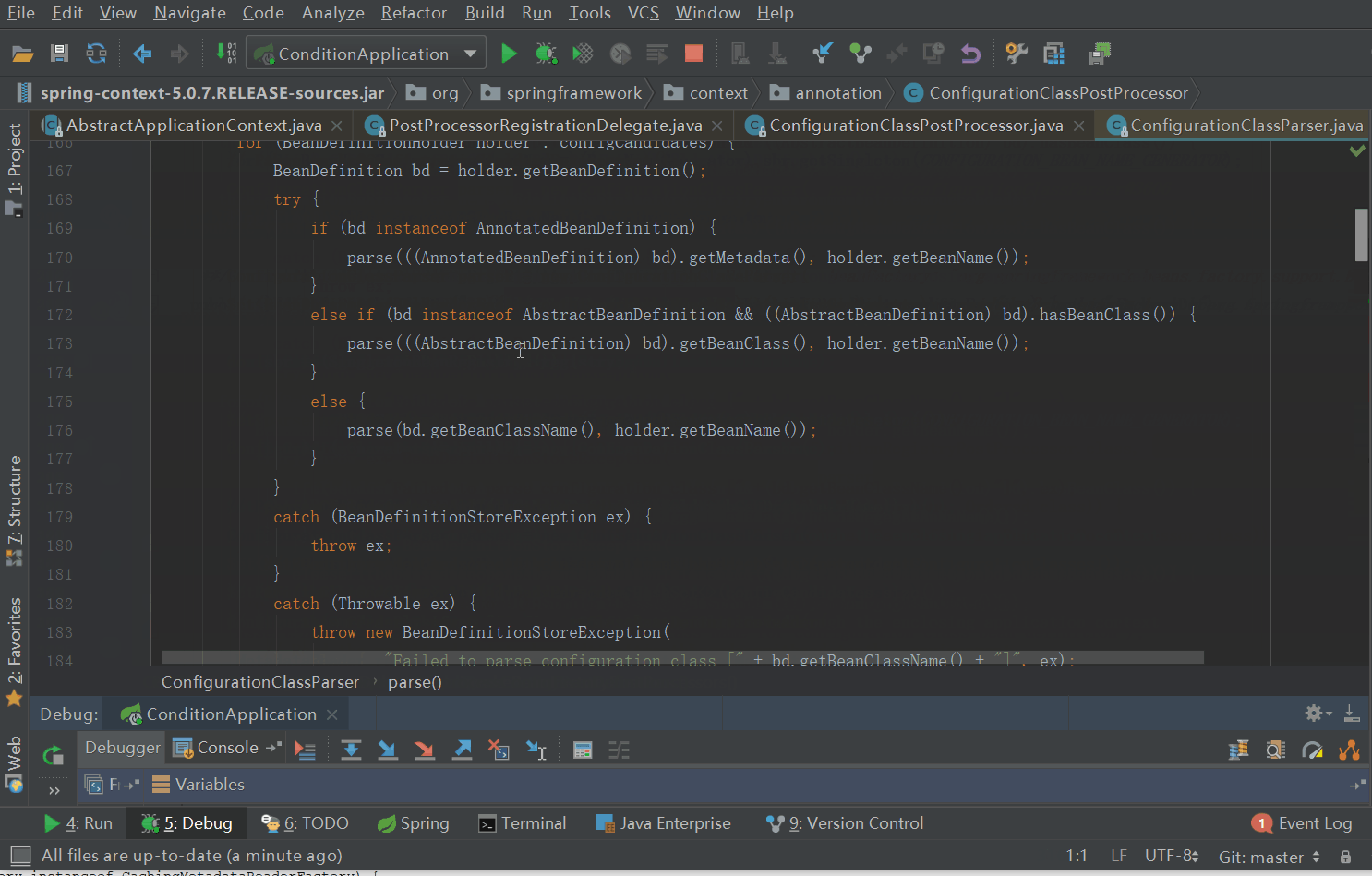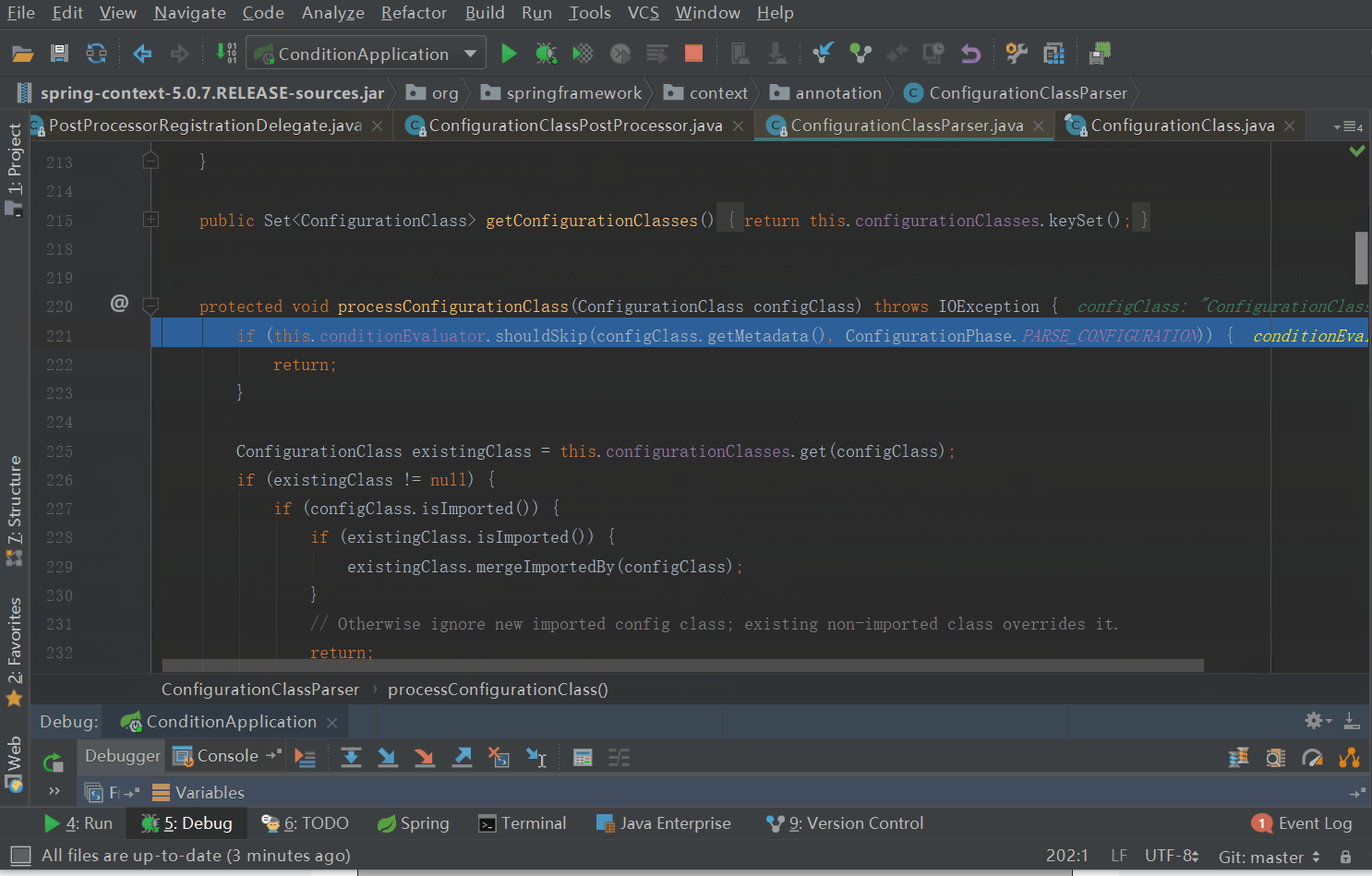
来到了processConfigurationClass方法,其详细代码如下


- protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass) throws IOException {
- // ConfigurationClass是否应该被skip
- if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
- return;
- }
- ConfigurationClass existingClass = this.configurationClasses.get(configClass);
- if (existingClass != null) {
- if (configClass.isImported()) {
- if (existingClass.isImported()) {
- existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass);
- }
- // Otherwise ignore new imported config class; existing non-imported class overrides it.
- return;
- }
- else {
- // Explicit bean definition found, probably replacing an import.
- // Let's remove the old one and go with the new one.
- this.configurationClasses.remove(configClass);
- this.knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals);
- }
- }
- // Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy. 递归处理configuration class和它的父级类
- // 也就说会递归处理我们的应用入口类:ConditionApplication.class,以及ConditionApplication.class的父级类
- SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass);
- do {
- sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass);
- }
- while (sourceClass != null);
- // 将满足条件的ConfigurationClass都放入configurationClasses集合中
- // 后续会加载configurationClasses集合中所有的ConfigurationClass中配置的bean定义
- this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
- }
View Code 其中shouldSkip方法如下


- /**
- * Determine if an item should be skipped based on {@code @Conditional} annotations.
- * @param metadata the meta data
- * @param phase the phase of the call
- * @return if the item should be skipped
- */
- public boolean shouldSkip(@Nullable AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, @Nullable ConfigurationPhase phase) {
- // 如果这个类没有注解修饰,或者没有被@Conditional注解(包括Conditional系列)所修饰,不会skip
- if (metadata == null || !metadata.isAnnotated(Conditional.class.getName())) {
- return false;
- }
- // 如果参数中沒有设置条件注解的生效阶段
- if (phase == null) {
- if (metadata instanceof AnnotationMetadata &&
- ConfigurationClassUtils.isConfigurationCandidate((AnnotationMetadata) metadata)) {
- return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION);
- }
- return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN);
- }
- // 要解析的配置类的条件集合,即@Conditional的value
- List<Condition> conditions = new ArrayList<>();
- for (String[] conditionClasses : getConditionClasses(metadata)) {
- for (String conditionClass : conditionClasses) {
- Condition condition = getCondition(conditionClass, this.context.getClassLoader());
- conditions.add(condition);
- }
- }
- // 对条件进行排序
- AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(conditions);
- // 遍历条件,逐个匹配
- for (Condition condition : conditions) {
- ConfigurationPhase requiredPhase = null;
- if (condition instanceof ConfigurationCondition) {
- requiredPhase = ((ConfigurationCondition) condition).getConfigurationPhase();
- }
- // 条件注解的生效阶段满足,一旦有条件匹配不成功,则返回true,skip此类
- if ((requiredPhase == null || requiredPhase == phase) && !condition.matches(this.context, metadata)) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
View Code 我们再回过头去看processConfigBeanDefinitions方法


- /**
- * Build and validate a configuration model based on the registry of
- * {@link Configuration} classes.
- * 验证@Configuration修饰的类,满足条件则构建成configuration model
- */
- public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
- List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
- String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
- for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
- BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
- if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) ||
- ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
- if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
- logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
- }
- }
- else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
- configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
- }
- }
- // Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
- if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
- return;
- }
- // Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
- configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
- int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
- int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
- return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
- });
- // Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
- // 检测自定义的bean生成策略
- SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
- if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
- sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
- if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
- BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
- if (generator != null) {
- this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
- this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
- }
- }
- }
- if (this.environment == null) {
- this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
- }
- // Parse each @Configuration class
- // 解析每一个被@Configuration修饰的class
- ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
- this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
- this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
- Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
- Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
- do {
- parser.parse(candidates); // 解析过程中会将满足条件的@Configuration class存放到configurationClasses中
- parser.validate();
- // 满足条件的@Configuration class 都存放在了parser的configurationClasses中
- Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
- configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
- // Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
- // 读取@Configuration class中的配置(各个@Bean),并创建对应的bean definition(后续创建bean实例会用到bean定义)
- if (this.reader == null) {
- this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
- registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
- this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
- }
- this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses); // 加载全部@Configuration class中的配置
- alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
- candidates.clear();
- if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
- String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
- Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
- Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
- for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
- alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
- }
- for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
- if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
- BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
- if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
- !alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
- candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
- }
- }
- }
- candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
- }
- }
- while (!candidates.isEmpty());
- // Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
- if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
- sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
- }
- if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
- // Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
- // for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
- ((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
- }
- }
View Code @Conditional是何时生效、如何生效的
这个问题再上面已经全部得到体现,Spring不会无脑的加载所有的@Configuration class,只会加载满足条件的@Configuration class,而@Conditional就是条件标志,至于条件匹配规则这有Condition提供;shouldSkip方法中用到Conditional和Condition,完成条件的匹配处理。
总结
1、@Configuration和@Bean组成了基于java类的配置,与xml中的<Beans>、<Bean>功能一致,Spring推荐java类的配置;
2、Condition与@Conditional实现了条件配置,只有满足了条件的@Configuration class和@Bean才会被注册到Spring容器;
3、Spring以我们的应用启动类为基础来递归扫描配置类,包括我们应用中的配置类、Spring自己的以及第三方的配置类(springboot集成的各种配置类(spring-boot-autoconfigure-xxx.RELEASE.jar下的spring.factories文件中的Auto Configure),还有pageHelper的自动配置,等等);前提是需要开启自动配置(@EnableAutoConfiguration)。
参考
SpringBoot源码分析之条件注解的底层实现
Spring 工具类 ConfigurationClassParser 分析得到